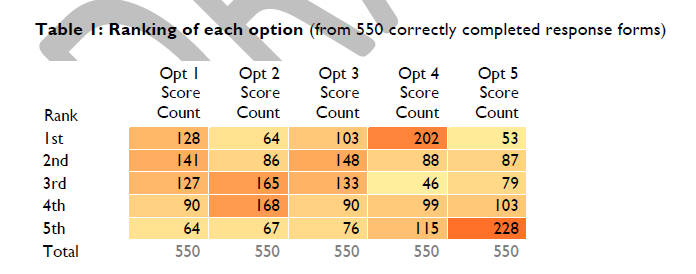
Example of traffic congestion that could happen in Winchfield
A new study by the Royal Town Planning Institute (RTPI), has shown that adding houses near railway stations in country areas could see a massive increase in car journeys each week to create additional congestion and delays on roads that are already overloaded. Of course there is a direct read across from the RTPI analysis to Hart Council’s proposals for a new town at Winchfield, that would inevitably impact Hartley Wintney, Hook, Odiham, Dogmersfield, Crookham Village, Church Crookham and Fleet.
We can estimate how many extra traffic movements there might be from a 5,000 house new town at Winchfield by looking at the Hampshire County Council transport contributions policy. They estimate 7 trips per average dwelling per day, which would lead to an extra 7 x 5,000 = 35,000 trips per day or 12.8m extra trips per annum on both minor country roads and our already congested wider road network.
Janet Askew, President of the Royal Town Planning Institute (RTPI), said:
“Quite apart from other good reasons why building in the green belt on such a scale might be opposed, these figures demonstrate a fundamental flaw in the reasoning that there is a quick fix and a sustainable solution to the housing crisis by putting large numbers of new homes close to railway stations.”
The RTPI press release went on to say:
“The view of the RTPI is that brownfield sites should be looked at as a priority for housing but not all brownfield sites will be suitable. The housing crisis is complex and will require a number of different policy solutions, such as increasing access to mortgage finance, improving transport and infrastructure, encouraging the house builders to build more homes, and a strong, delivery focussed planning system. Major proposals for new homes, whether they are in the green belt or on brownfield sites, must be preceded by adequate investment in schools, health, transport and other infrastructure, and planned in a strategic and holistic way, with up to date local plans being critical.”
Of course this is consistent with what We Heart Hart has been saying for many months, but Hart Council will not consider adding a brownfield development option into the Local Plan process; won’t look at our alternative 5-point plan and won’t even establish a register of brownfield sites.
The full text of the RTPI press release is shown below:
Using commuting data from the 2011 Census the Royal Town Planning Institute (RTPI), has today published analysis which finds that adding 1 million homes near railway stations in the Metropolitan London green belt area could see 3.9-7.5 million car journeys each week added to roads which are already struggling with congestion and delays. These findings – Building in the green belt? A report into commuting in the Metropolitan green belt challenge the assumption that building in the green belt around railway stations would see the majority of new residents using the train to get to jobs in London and could therefore be easily accommodated.
Over the past year various think tanks, academics and policy commentators have considered whether green belt boundaries around London should be relaxed in order to ease the housing crisis. These proposals often suggest the release of green belt land within easy walking or cycling distance of key railway stations, land which could provide space for figures upwards of 1 million homes. The assumption behind these proposals is that the majority of new residents will commute by rail to jobs in central London, enabling sustainable housing growth in the wider Metropolitan region without placing excessive strain on existing roads. However the implications of growth on commuting patterns is difficult to predict without looking at those already living in the green belt. Where are these residents travelling for work, and what methods of transport are they using to get there?
The RTPI examined commuting data for five medium-sized towns within the existing Metropolitan green belt, towns which are centred around railway stations and have direct connections to central London. We found that in these five towns, only 7.4% of commuters actually travel to inner London by train on a regular basis, despite living within easy walking or cycling distance of a station. The majority of commuters (72%) instead travel by private vehicle, mostly driving to jobs within their hometown and to other places not in London.
Janet Askew, President of the Royal Town Planning Institute (RTPI), said:
“If 1 million new homes were built in the green belt in this way, this is likely to result in a huge increase in the number of car journeys being made across the green belt to work, and between schools health facilities and stations”.
“Quite apart from other good reasons why building in the green belt on such a scale might be opposed, these figures demonstrate a fundamental flaw in the reasoning that there is a quick fix and a sustainable solution to the housing crisis by putting large numbers of new homes close to railway stations. While it is difficult to predict exactly future commuting patterns, the overwhelming evidence is that people will use their cars and this will result in vastly increased numbers of car journeys in and through the green belt.”
Trudi Elliott, Chief executive of the Royal Town Planning Institute (RTPI), said:
“The outcome of the analysis was surprising given the range of voices calling for housing around railway stations in the green belt. Our data shows, using one region of the green belt, just how complex the issue of commuting patterns is and how unpredictable they are likely to be in the future. The green belt is an important planning tool. Our findings demonstrate that it is vital to have an evidence base before you make major policy.”
The view of the RTPI is that brownfield sites should be looked at as a priority for housing but not all brownfield sites will be suitable. The housing crisis is complex and will require a number of different policy solutions, such as increasing access to mortgage finance, improving transport and infrastructure, encouraging the house builders to build more homes, and a strong, delivery focussed planning system. Major proposals for new homes, whether they are in the green belt or on brownfield sites, must be preceded by adequate investment in schools, health, transport and other infrastructure, and planned in a strategic and holistic way, with up to date local plans being critical. Any development in the green belt continues to need rigorous justification under the planning system and there are many checks and balances in place.
The five towns in the RTPI analysis were: Hemel Hempstead, High Wycombe, Watford, Maidenhead and Bracknell.
The RTPI is also publishing today a short YouTube film and a new public information note explaining the history, background and purpose of the green belt. A recent Ipsos Mori poll found 71% of all age groups knew just a little/ heard of but know nothing/never heard of green belt land. Among the under 34s this was 85% and among the under 24s the figure was 92%.